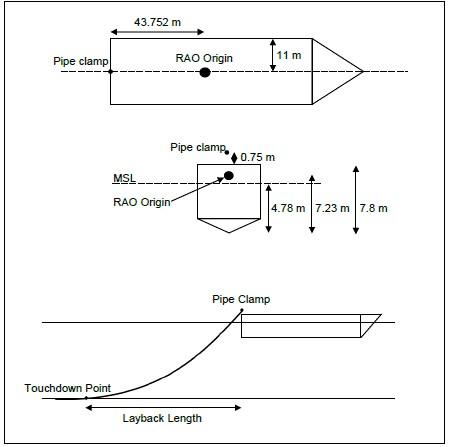
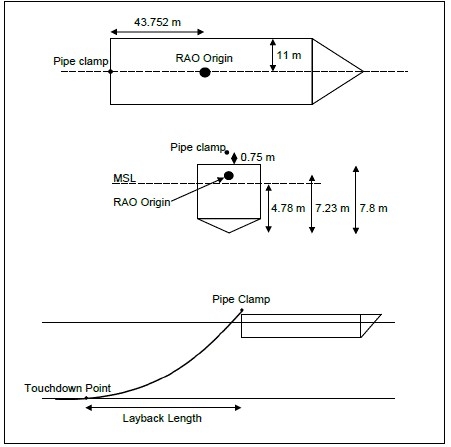
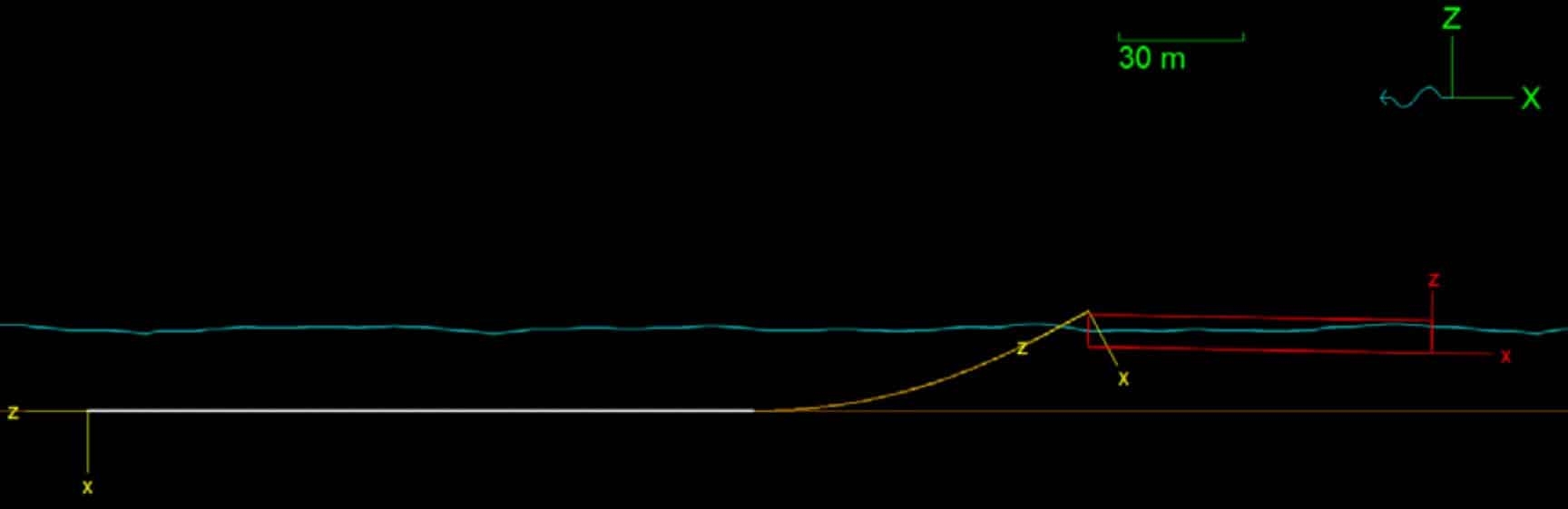
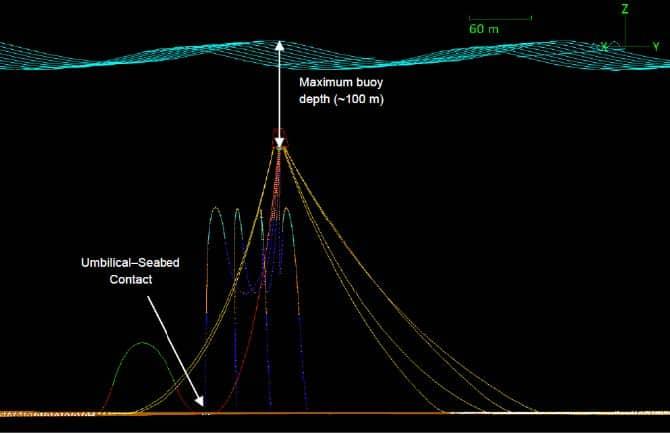
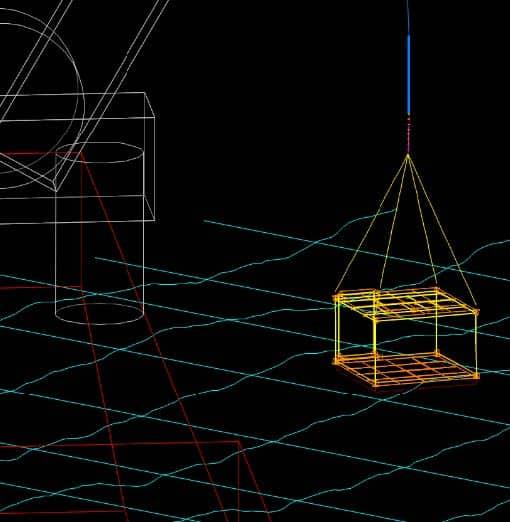
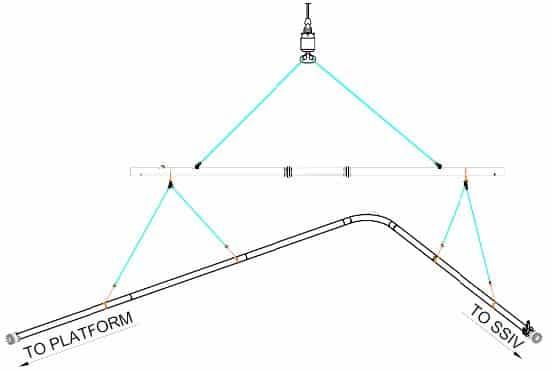
Atteris conducted both static and dynamic pipelay analyses over a range of pipe sizes (6-in to 12-in), water depths (7 m to 250 m) and sea states (up to 2 m Hs) to evaluate the feasibility of the proposed H-lay concept. The analyses considered a 3-hour irregular sea state (simulated using JONSWAP) and was performed to cover the period when the most severe sea elevation occurs. For each load case analysed, the maximum von Mises stress, angle of departure and difference in arc length to layback distance were recorded.
Atteris also performed sensitivity analyses to study the effects of increased clamp tension, reduced wall thickness and different peak wave periods on the results. From the analyses, it was concluded that the proposed H-lay concept is suitable within the parameters analysed. It was apparent from the analyses that a key issue in ensuring the integrity of the pipeline during lay is control of the stresses at clamp locations. Atteris made recommendations that would reduce the localised stress at the clamp location i.e. releasing the pitch restraints on the clamp and introducing a pipe support that could improve peak pipe stresses. However, it was also noted that operational constraints may prove to be the limiting factor rather than pipe stresses considering the range of motion of the clamped pipe end.